HEAT EXCHANGERS
Industrial heat exchangers enable the transfer of thermal energy between two or more fluids at different temperatures without direct contact. They are key equipment for heating, cooling, condensing, evaporating, or recovering heat within industrial processes, improving energy efficiency and reducing operating costs.
At BOIXAC, we design custom-built heat exchangers, precisely adapted to the real operating conditions of each industrial process across sectors such as food processing, chemical, pharmaceutical, energy, paper, steelmaking, oil & gas (refineries), wastewater treatment, glass, and ceramics, among many others.
This page serves as the canonical guide to BOIXAC industrial heat exchangers, bringing together all available models, typologies, and applications.
What is an industrial heat exchanger?
A heat exchanger is equipment designed to transfer heat from one fluid to another in a controlled and safe manner, optimizing the thermal performance of the process while complying with current industrial regulations and standards.
Main objectives
Energy recovery
Reduction of energy consumption
Process stability
Temperature control
Increased industrial sustainability
How are industrial heat exchangers classified?
There are several engineering-based criteria used to classify heat exchangers.
By type of fluids
Gaseous fluids
Liquid fluids
Solid fluids (granulated or bulk)
High- or low-viscosity fluids
Corrosive or contaminating fluids
By mechanical construction
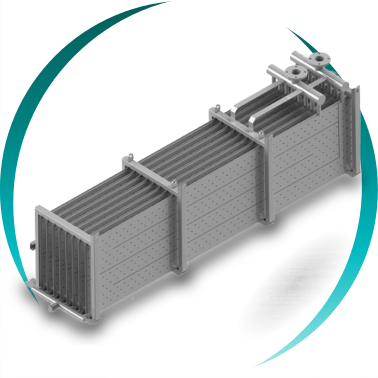
Tubular heat exchangers
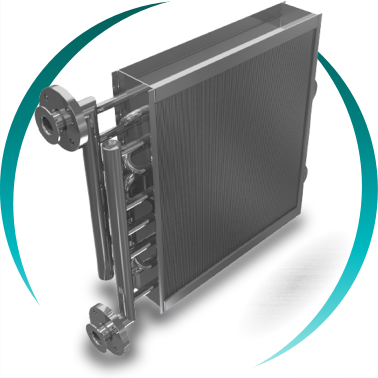
Plate heat exchangers
Tube coils
Spiral heat exchangers
Custom-designed special equipment
By industrial application
Waste heat recovery
Product cooling
Fluid preheating
Condensation and evaporation
HVAC and industrial climate control
BOIXAC industrial heat exchanger models
At BOIXAC, we structure heat exchangers into technical families, each optimized for specific operating conditions. These families form the core of our industrial heat exchanger cluster.
By operating principle
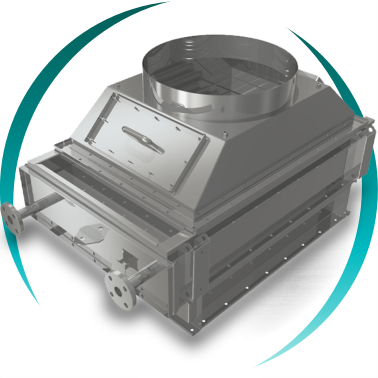
Gas-to-gas heat exchanger
Designed for the treatment of combustion or process gases at high temperature, enabling thermal energy recovery in harsh industrial environments and improving overall system efficiency. Typical applications:
- Combustion flue gases
- Air preheating
- Heat recovery units
- Recuperative thermal oxidizers (RTO)
By construction
Special equipment
How to choose the right heat exchanger model
Selection depends on the type of fluid, temperatures, pressure, process objective, and installation conditions.
Identify fluid types and properties
Define operating temperatures and pressures
Determine the thermal objective of the process
Evaluate available space and maintenance requirements
Select materials and applicable standards (PED, ATEX, hygiene)
Common industrial applications
Heat exchangers are used in applications such as:
Cooling of chemical products
Preheating before reactions
Vapor condensation
Energy recovery
Industrial HVAC
Food and pharmaceutical processes
Custom heat exchanger manufacturing
At BOIXAC, we design tailor-made solutions, optimized for:
Energy efficiency
Durability and reliability
Ease of maintenance
Regulatory compliance
Agility
Service
Strength
Quality
FAQs
What is the best industrial heat exchanger model?
There is no universal model. It depends on the fluid, temperatures, pressure, available space, and process objective.
In industrial environments, the optimal solution is usually a custom-designed heat exchanger.
What types of heat exchangers exist?
Gas-to-liquid, gas-to-gas, liquid-to-liquid, solid-to-liquid, tubular, plate, coil, and special heat exchangers.
This classification allows selecting the most efficient model according to real operating and maintenance conditions.
What is the difference between a tubular heat exchanger and a plate heat exchanger?
Tubular heat exchangers better withstand high pressures and temperatures, while plate heat exchangers offer higher efficiency in a smaller footprint.
Tubular heat exchangers are especially suitable for processes with high pressures and temperatures, dirty fluids, or severe conditions. Plate heat exchangers, on the other hand, provide very efficient heat transfer in a compact volume, facilitating maintenance and cleaning in applications with clean fluids.
When is a custom heat exchanger necessary?
When a standard unit does not meet process requirements.
Corrosive fluids, high pressure, strict regulations, or special geometries require customized solutions.
What materials are used in industrial heat exchangers?
Carbon steel, stainless steel, special alloys, and corrosion-resistant materials.
Material selection depends on fluid type, temperature, pressure, and potential corrosion. Stainless steels are common in food and pharmaceutical industries, while special alloys are used in demanding chemical or petrochemical environments.
Which industrial applications use heat exchangers?
Chemical, food, pharmaceutical, HVAC, energy, and general industrial processes.
Heat exchangers are essential for energy recovery, product cooling, fluid preheating, vapor condensation, and industrial climate control systems. Each sector has specific requirements that determine the type of exchanger used.
How does energy efficiency affect heat exchanger selection?
Higher efficiency reduces energy consumption and operating costs.
An efficient heat exchanger improves heat transfer with lower losses, optimizes process performance, and reduces energy impact. In industrial environments, this translates into significant savings and greater sustainability.