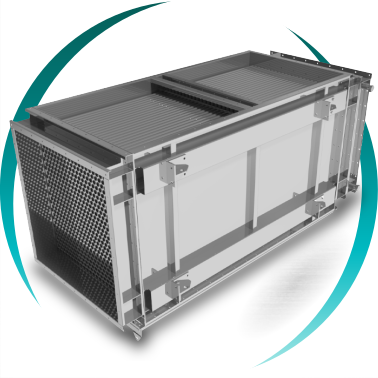
GAS-GAS HEAT EXCHANGER
A gas-to-gas heat exchanger is an industrial device that allows the recovery of thermal energy between two independent gas streams through a solid surface, without fluid mixing, improving process energy efficiency, reducing fuel consumption, and minimizing associated emissions.
Gas-to-Gas energy recovery with BOIXAC industrial engineering
At BOIXAC, we design, engineer, and optimize custom industrial gas-to-gas heat exchangers, focused on recovering waste heat, improving energy efficiency, and reducing operational costs in demanding industrial processes.
Our solutions enable the recovery of heat contained in hot gases — air, flue gases, nitrogen, or other process gases — and its controlled transfer to a second independent gas stream. In this way, energy losses are transformed into reusable thermal resources, with a direct impact on process performance and the facility’s carbon footprint.
This page serves as the central node of the BOIXAC gas-to-gas cluster, providing a global, conceptual overview of the technology and linking to specific solutions: air-to-air, air-to-flue gas, and cross-flow plate recuperators, where construction and application details are presented.
Conceptual engineering applied to Gas-to-Gas heat exchangers
At BOIXAC, we do not use standard equipment. Each gas-to-gas heat exchanger is conceptualized based on a thorough technical analysis of the process, aiming to define the technology that maximizes return on investment (ROI) and ensures long-term reliability.
Key parameters analyzed include:
Inlet and outlet temperatures of the gas streams
Mass and volumetric flow rates
Chemical composition and presence of contaminants
Allowable fouling levels
Maximum allowable pressure drops
Expansion and mechanical stress conditions
Sealing requirements between streams
Cleaning and maintenance needs
This approach allows precise selection of the optimal gas-to-gas technology, avoiding oversizing, operational problems, or performance loss over time.
How a Gas-to-Gas heat exchanger works
The operation of a gas-to-gas heat exchanger is based on three fundamental steps:
The hot gas stream transfers its thermal energy to the separating surface.
Heat is conducted through the exchanger material.
The cold gas stream absorbs this energy by convection, increasing its temperature.
At no point do the gases come into direct contact, ensuring functional separation of the streams and process safety.
Direct benefits for energy efficiency
Integrating a gas-to-gas heat exchanger produces direct, measurable, and quantifiable impacts:
Reduced energy consumption through reuse of residual heat
Preheating or precooling of gases entering reactors, furnaces, or process chambers
Decreased CO₂ and greenhouse gas emissions
Lower operational costs, with typical ROI between 3 and 12 months depending on the application
Industrial applications of Gas-to-Gas heat exchangers
Combustion air preheating
Typical application of air-to-flue heat exchangers. Exhaust gases from furnaces, boilers, or turbines (200–600 °C) transfer energy to the incoming combustion air, improving flame efficiency and reducing fuel consumption by 10–30%.
Industrial ventilation and HVAC
Using air-to-air exchangers, hot extracted air transfers energy to incoming outside air, reducing heating or cooling demand in industrial buildings.
Chemical and pharmaceutical processes
Control and stabilization of process gas temperatures, recovering internal energy while ensuring thermal homogeneity and reaction stability.
Gas effluent treatment
Pre-cooling of gases before filters, scrubbers, or purifiers, protecting critical equipment and recovering energy for other process stages.
Industrial drying
Recovery of exhaust air heat to preheat fresh air, reducing the overall energy consumption of drying systems.
Which Gas-to-Gas heat exchanger do I need for my process?
This page provides a global overview of gas-to-gas heat exchangers. Construction and functional details are explored on the specific technology pages below:
Air-to-Air Heat Exchanger
Technology based on expanded tubes against terminal plates, with no welding between tubes and plates. Ideal for high temperatures and heavy fouling.
Key Features
Approx. 99% tightness
High fouling tolerance
No welds → minimal mechanical stress
Excellent high-temperature performance
Main Advantages
Ideal for dusty or particle-laden industrial environments
Easy mechanical cleaning
Long service life under severe conditions
Air-to-Flue gas heat exchanger
Welded tubes on terminal plates ensure 100% tightness. Ideal for combustion gases or where absolute separation is required.
Key Features
Complete separation between air and flue gas
Designed for combustion gases
High-temperature resistance
Smooth anti-fouling tubes
Main Advantages
Maximum energy recovery
Protection of downstream equipment
Direct reduction of fuel consumption
Critical design and selection factors
Temperature difference (ΔT)
Mass and volumetric flow rates
Allowable pressure drop
Chemical composition and acid dew point
Cleaning and maintenance strategy
Available space and installation criteria
Heat recovery
units
Empower
your energy
FAQs
Which material is best for an air-to-flue gas exchanger?
Depends on operating temperature, flue gas composition, and corrosion or acid condensation risk.
For natural gas or diesel flue gases with low sulfur content at 400–500 °C, AISI 316L is usually suitable if acid condensation is avoided. For higher temperatures or strongly oxidizing environments, high-temperature alloys like AISI 309 or 310 are often used. At BOIXAC, final selection is based on specific corrosion and condensation analysis.
Are gas-to-gas exchangers easy to clean?
Yes, if designed with cleaning in mind.
Cleaning is defined during the conceptual phase with access ports, smooth tubes, wide passages, and, if necessary, automatic cleaning systems. In critical applications, modular designs can be considered for maintenance ease.
What energy savings can I expect?
Typically between 10% and 30%.
Savings depend on ΔT, flow rates, and annual operating hours. In ventilation systems with heat recovery, demand reduction can reach 40–70%. Exact calculation requires a specific energy assessment.
What is the service life of a gas-to-gas heat exchanger?
Very long with proper design.
Service life mainly depends on corrosion, erosion, and fouling. Correct material selection and preventive maintenance ensure stable thermal performance for many years.
Which is more efficient: air-to-air or air-to-flue?
Depends on the process.
Both can achieve efficiencies above 70–80%. Selection depends on required tightness, fouling, corrosion, thermal expansion, and maintenance requirements. At BOIXAC, we define the optimal technology case by case.