INDUSTRIAL HEAT RECOVERY UNIT FOR BOILERS AND EXHAUST GASES
An industrial heat recovery unit is a thermal engineering system designed to recover residual thermal energy from hot exhaust gases generated by an industrial process and reuse it safely, in a controlled and continuous manner, within the same process or in auxiliary processes.
The objective is to reduce primary fuel consumption, operating costs and CO₂ emissions, with typical payback periods ranging from 3 to 12 months in real industrial applications.
Within industrial energy efficiency solutions, the heat recovery unit is one of the technologies with the best cost–benefit ratio when recoverable waste heat and a compatible thermal demand are available.
Industrial heat recovery unit: energy that is no longer wasted
In industrial processes involving combustion, furnaces, drying systems, boilers, engines or thermal generation, a significant portion of the consumed energy is inevitably discharged with the exhaust gases.
This unrecovered residual energy represents:
Direct and recurring energy costs
Unnecessary increases in CO₂ emissions
Loss of overall process efficiency
The industrial heat recovery unit makes it possible to convert previously wasted energy into useful energy, improving system performance without altering production capacity or operational safety.
At BOIXAC, we conceive heat recovery units as applied engineering systems, not as standard off-the-shelf equipment. Each project is designed according to the plant’s real operating conditions.
What is an industrial heat recovery unit?
An industrial heat recovery unit is a gas–liquid heat exchanger that utilizes residual heat from exhaust gases to heat a useful process fluid, reducing energy consumption, operating costs and emissions without affecting production.
In practical terms: energy that was previously lost becomes measurable industrial value.
Key benefits of a heat recovery unit
Increase in overall process energy efficiency
Reduction in primary fuel consumption
Direct and quantifiable reduction in CO₂ emissions
Improved industrial competitiveness
Energy recovery with minimal operational risk
Operation of a gas–liquid heat recovery unit
The industrial heat recovery unit operates through the controlled transfer of heat between two fluids at different temperatures, without direct contact.
Operating principle
Hot residual gases flow through the gas side of the heat exchange bundle
The receiving fluid circulates through the liquid side
Heat is transferred through the metallic surface
The gases are discharged at a lower temperature
Typical receiving fluids
Process water
Superheated water
Thermal oil
Steam (specific configurations)
This configuration reduces primary energy demand without compromising process stability.
Heat recovery unit and economizer: key differences
An industrial economizer is a specific type of heat recovery unit, generally integrated into boilers, with the specific function of preheating the feedwater.
Essential difference
Economizer: application specific to boilers
Industrial heat recovery unit: broader concept applicable to furnaces, engines, turbines, industrial drying and continuous processes
The objective is always the same: to maximize the available energy recovery from the process.
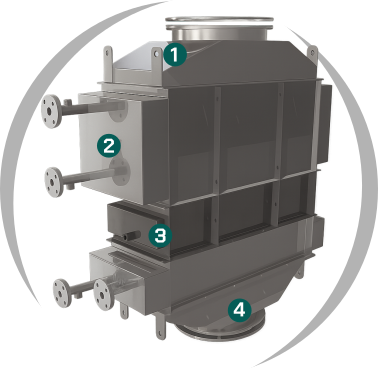
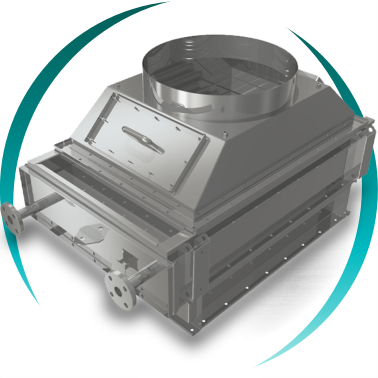
1- Inspection opening. 2- Extraction system. 3- Condensate collection tray. 4- Transition (rectangular to circular)
Real industrial operating conditions for economizers
BOIXAC heat recovery units are designed to operate in demanding industrial environments:
Gases containing dust, ash or solid particles
High fouling levels
Gas temperatures up to 850 °C
Fuels: biomass, natural gas, fuel oil, diesel
Adapting the design to these conditions is essential to ensure stable performance and extended service life.
BOIXAC applied engineering
At BOIXAC, we do not supply generic equipment. Each heat recovery unit is the result of:
Specific thermal calculation
Real analysis of gas composition and operating regime
Fouling assessment and maintenance strategy
Integration with existing installations
This approach ensures that calculated performance corresponds to real operating performance, not just theoretical values.
Design focused on maintenance and availability
BOIXAC heat recovery units incorporate:
Robust structures resistant to thermal expansion
Accessible inspection and cleaning openings
Heat exchange bundle extraction systems
Adaptation to existing stacks and ducts
Thermal insulation using refractory materials
Flow control through by-pass systems, dampers and regulation
The result is high operational availability and sustained performance throughout the entire service life.
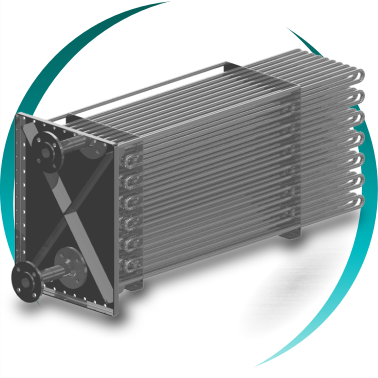
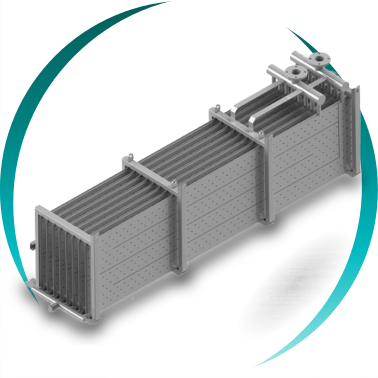
Heat exchange bundle configurations
Depending on temperature, pressure, humidity and fouling level:
Continuous finned tubes
Helical finned tubes
Plain tubes
Pillow plate systems
In dirty gas applications, ease of cleaning and operational stability take priority over maximum theoretical heat transfer surface.
When is a heat recovery unit truly viable?
Highly recommended when:
Gas temperatures > 180–200 °C
Operation during many hours per year
Existence of reusable thermal demand
Integration possible without operational risk
Not recommended when:
Highly intermittent production
Absence of thermal consumption
These criteria prevent inefficient investments and strengthen the technical decision-making process.
Typical ROI
Efficiency
Temperature
Welds
FAQs
What is an industrial heat recovery unit?
An industrial heat recovery unit is a heat exchanger that recovers heat from hot residual exhaust gases and reuses it in the production process, reducing energy consumption, costs and emissions.
In industrial environments, large amounts of energy are discharged with exhaust gases. A heat recovery unit makes it possible to utilize this energy to heat water, thermal oil or generate steam, improving overall process efficiency without affecting production or operational safety.
What is the difference between a heat recovery unit and an economizer?
An economizer is a heat recovery unit specifically designed for boilers; an industrial heat recovery unit can be applied to multiple processes.
The economizer is mainly used to preheat boiler feedwater. The heat recovery unit concept is broader and includes applications in furnaces, engines, turbines, industrial drying and continuous processes, always with the goal of maximizing system energy recovery.
Can heat recovery units be used with dirty or dusty gases?
Yes, provided that the design is adapted to the gas fouling level.
In processes with dust, ash or solid residues, the heat recovery unit design must prioritize plain tubes, easy access for cleaning and heat exchange bundle extraction systems. Ignoring fouling is one of the main causes of medium-term performance loss.
What is the most important criterion in the design of a heat recovery unit?
Adaptation to the real operating conditions of the process.
The key criterion is not maximizing theoretical heat transfer surface area, but designing the system considering operating regime, fouling, maintenance, thermal expansion and operational availability. This ensures sustained performance, not just initial theoretical values.
What impact does a heat recovery unit have on CO₂ emissions?
It directly reduces CO₂ emissions by lowering fuel consumption.
Heat recovery reduces primary energy demand. Burning less fuel leads to a direct, measurable and verifiable reduction in CO₂ emissions associated with the industrial process, contributing to decarbonization objectives.