INDUSTRIAL STEAM HEAT EXCHANGER
A steam heat exchanger is a critical component in the thermal management of industrial processes where steam acts as the primary energy vector. These units enable the controlled, safe, and efficient transfer, conditioning, or recovery of thermal energy, even in environments with high pressures, extreme temperatures, and severe operating conditions.
High-efficiency, high-pressure steam heat exchangers
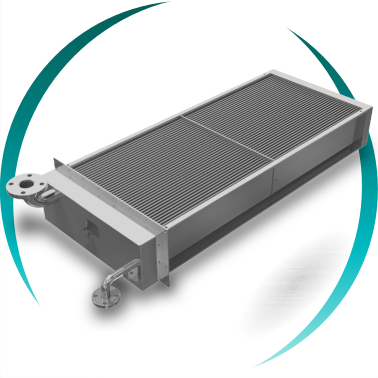
At BOIXAC, we propose thermal exchange solutions based on tubular coils with helical fins, continuous fins or plain tubes, designed to operate with steam under demanding pressure and temperature conditions, ensuring efficient, controlled and safe heat transfer in complex industrial environments.
What is a steam heat exchanger?
A steam heat exchanger is an industrial unit that transfers thermal energy from steam to another fluid or conditions steam within a process, improving energy efficiency and thermal control.
It is a heat exchange device specifically engineered to operate with steam in different thermodynamic states. It can be used to heat fluids, dry products, superheat steam, control condensation, or recover residual heat, reducing overall energy consumption and stabilizing industrial processes.
Industrial applications of steam heat exchangers
BOIXAC steam heat exchangers are widely used in:
Energy and cogeneration
Chemical and process industries
Pulp and paper industry
Metallurgy and heavy industry
Food and beverage processing
Industrial agriculture and greenhouses
Industrial drying systems
Boilers and thermal installations
Fluid treatment and purification
Industrial HVAC systems
Marine and offshore installations
BOIXAC technology in steam heat exchangers
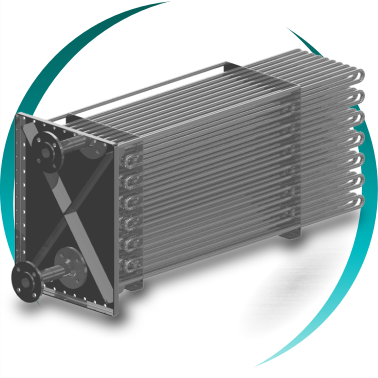
Tubular coils for high-demand steam applications
Tubular coils for steam heat exchangers are engineered to withstand high pressures and extreme temperatures, with operating capabilities of up to 950 °C, depending on design and selected materials.
Available configurations:
Plain tubes
Helical finned tubes
Continuous finned tubes
Custom geometries based on space and flow requirements
This geometric flexibility allows maximum heat transfer, minimal pressure drop, and seamless integration into constrained spaces.
High-durability industrial materials
Materials are selected based on:
Operating temperature
Service pressure
Chemical environment
Thermal cycling
Fouling tendency
Common materials include:
Carbon steel
Stainless steel AISI 304
Stainless steel AISI 316
Duplex steel
Hastelloy
Titanium
This selection ensures mechanical strength, thermal stability, and excellent performance in corrosive environments, including marine or chemically aggressive applications.
Energy recovery with steam and flash steam
At BOIXAC, we develop advanced energy recovery solutions using steam heat exchangers designed to harness residual heat from flash steam generated during depressurization processes.
Finned-tube heat exchangers are particularly effective for:
Live steam systems
Industrial energy recovery
Thermal consumption optimization
Each project begins with a detailed technical analysis of flow rates, temperatures, pressures, and spatial constraints, aiming to achieve maximum thermal performance with minimal pressure loss.
High-pressure steam heat exchanger – HT
The HT steam heat exchanger is designed for critical applications requiring:
Drying of wet steam
Conversion of saturated steam into dry steam
Superheating steam for demanding processes
Key features
Operating temperature: up to 950 °C
High structural robustness
Thermal stability under extreme conditions
Continuous operational reliability
Precision, quality, and industrial control
BOIXAC steam heat exchangers are manufactured under strict industrial standards, including:
Dimensional inspections
Leak and tightness testing
Verification before and after assembly
This process ensures reliability, safety, and production precision, even in installations with severe operating conditions.
Typical ROI
3-12 months
Resistance
up to 950ºC
Warranty
2 years
Reduced
energy consumption
FAQs
What is the difference between saturated, wet, and superheated steam?
It depends on water content and temperature relative to the saturation point.
Saturated steam is in equilibrium with water at a given pressure. Wet steam contains water droplets that reduce efficiency and may cause erosion. Superheated steam is dry steam heated above the saturation point, making it ideal for high-demand industrial processes.
What is the maximum operating temperature of a steam heat exchanger?
Up to 950 °C, depending on design and materials.
High-end industrial steam heat exchangers can operate at very high temperatures when mechanical design, materials, and process conditions allow, particularly in HT applications.
What is flash steam energy recovery?
It is the recovery of residual heat generated during depressurization.
When a hot fluid is suddenly depressurized, part of its energy is released as flash steam. Using an appropriate heat exchanger, this energy can be recovered and reused, significantly improving overall system efficiency.
What is the difference between plain tubes and finned tubes?
Finned tubes provide a larger heat transfer surface.
Plain tubes are used for direct heat transfer, while finned tubes increase the available surface area, improving efficiency in energy recovery processes or gas-side heat exchange.
Can steam heat exchangers be installed in confined spaces?
Yes, through custom engineering.
By tailoring coil geometry, flow arrangement, and exchanger configuration, high-performance steam heat exchangers can be integrated into limited spaces without compromising thermal efficiency.