TUBULAR HEAT EXCHANGER FOR DIFFICULT FLUIDS
A tubular heat exchanger is an industrial heat exchanger specifically designed to handle complex fluids with demanding rheological behavior, where precise flow control and direct mechanical cleaning are required.
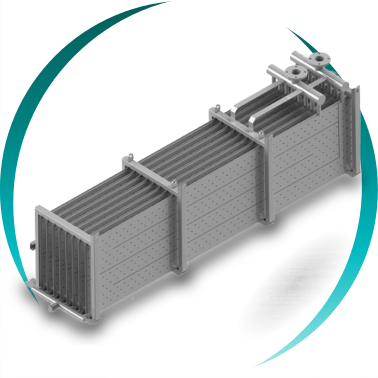
The BOIXAC tubular heat exchanger is a multitubular, modular and dismantlable heat transfer solution, conceived for industrial processes in which fluid behavior is the determining design factor.
Unlike heat exchangers designed for clean or low-viscosity fluids, the BOIXAC tubular exchanger is optimized for:
Viscous and pasty fluids
Non-Newtonian fluids
Streams containing solids, fibers or sediments
Processes with a high risk of fouling
The design criterion is not compactness, but operational reliability and effective cleaning.
When to choose a tubular heat exchanger; decision criteria
It is the best option when:
The fluid changes viscosity with temperature or shear
Solids, fibers, particles or sediments are present
The process does not allow excessive pressure losses
Direct mechanical cleaning is essential
It is not the optimal solution when:
The fluid is clean and stable
Maximum compactness is a priority
The process allows exclusive CIP without mechanical access
This definition eliminates overlap with other technologies within the cluster.
Construction design focused on the rheological behavior of the fluid
The BOIXAC tubular heat exchanger is based on a modular multitubular architecture, with tubes interconnected by removable bends, allowing:
Direct access to each tube
Individual mechanical cleaning
Adaptation of the flow path and effective length
Assembly and disassembly in confined spaces
Manufacturing materials
Selected according to chemical compatibility and mechanical requirements, the main materials are:
AISI 304 stainless steel
AISI 316 stainless steel
Optimization for non-Newtonian and heavily loaded fluids
Fluid behavior determines the real performance of a tubular heat exchanger. The BOIXAC design allows precise control of:
Flow regime (laminar / transitional / turbulent)
Shear rate inside each tube
Overall heat transfer coefficient
Tendency to fouling and scaling
Operational results
Stable heat transfer in complex fluids
Reduced fouling
Sustained energy efficiency over time
Operational continuity of the process
Key advantages of the tubular or hairpin heat exchanger
Tubular or hairpin heat exchangers provide:
High fouling tolerance, ideal for fluids with impurities, fibers, particles or sediments
Direct access to the inside of the tubes, facilitating mechanical cleaning
Modular, component-based design suitable for installation in confined spaces
Easy disassembly and inspection
Reliable operation in continuous or batch processes
When the process requires handling very large solids, long fibers or extremely dirty streams, a tubular heat exchanger specifically designed to maximize tolerance to severe fouling is recommended.
Industrial applications of the tubular heat exchanger
The BOIXAC tubular heat exchanger is particularly suitable for sectors working with difficult fluids where other technologies show limitations.
Food industry
Processes with high hygienic requirements, viscous fluids and frequent cleaning needs:
Vegetable and animal fats and oils
Fermented beverages (wine, beer, cider, alcohol)
Sauces, stir-fries, emulsions and food preparations
Purées, creams, concentrates, syrups and molasses
Juices, pulps and fruit concentrates
Dairy products and derivatives
Wastewater and environmental treatment
Designed to handle highly loaded fluids:
Primary, secondary and digested sludge
Livestock slurry
Industrial wastewater
Streams with sediments and organic matter
Preheating prior to anaerobic digestion or drying
Chemical industry
Viscous or non-Newtonian products
Solid-liquid suspensions
Resins, polymers, glues and adhesives
Streams with scaling or crystallization
Energy recovery in chemical processes
Pharmaceutical and biotechnology industry
Viscous solutions
Suspensions and emulsions
Fermentation broths
By-products with solid content
Other sectors
Pulp and paper (pulp, fibers, liquors)
Cosmetics (creams, gels, emulsions)
Energy, biomass and animal feed
This wide range of applications confirms the specialized and versatile nature of the BOIXAC tubular heat exchanger.
Typical ROI
3-12 months
Ideal for
solids, fibres & residues
Warranty
2 years
Design
modular
FAQs
Why choose BOIXAC as a tubular heat exchanger supplier?
For modular design, industrial experience and focus on difficult fluids.
BOIXAC provides tubular heat exchangers based on applied engineering criteria, adapted to the real behavior of the fluid and focused on long-term reliability. This specialization enables robust, efficient and cost-effective solutions for industrial processes where other technologies fail.
What is a tubular heat exchanger?
A tubular heat exchanger is a heat exchanger designed with multiple tubes that enable heat transfer in viscous, non-Newtonian or solid-laden fluids, facilitating mechanical cleaning and reducing fouling.
The BOIXAC multitubular heat exchanger uses a modular architecture made up of removable tubes, allowing operation with complex fluids while maintaining thermal efficiency. It is especially suitable when fluid rheology, the presence of solids or the risk of scaling makes other heat exchange technologies unfeasible.
When is a tubular heat exchanger recommended?
It is recommended when the process handles viscous, sticky fluids with fibers, sediments or a high risk of fouling.
The tubular heat exchanger is the best option when the fluid has complex rheology, viscosity variations or solid loading, and when frequent mechanical cleaning is required. It is common in processes where operational reliability and process continuity are more important than extreme equipment compactness.
What advantage does a multitubular heat exchanger have over other technologies?
It allows direct tube cleaning and maintains performance with difficult fluids.
Unlike heat exchangers designed for clean fluids, the dismantlable multitubular design provides direct access to the inside of the tubes, drastically reducing the impact of fouling, simplifying maintenance and ensuring consistent thermodynamic performance even under severe operating conditions.
How does fluid rheology influence tubular design?
Rheology determines flow regime, heat transfer and fouling tendency.
In non-Newtonian or variable-viscosity fluids, the tubular heat exchanger allows adjustment of velocities, flow regimes and hydraulic conditions per tube. This rheological control is key to reducing scaling, stabilizing the heat transfer coefficient and ensuring reliable system operation.
What type of maintenance does a tubular heat exchanger require?
It requires simple maintenance with direct mechanical cleaning.
Thanks to its dismantlable design, the BOIXAC tubular heat exchanger allows rapid and safe inspection, cleaning and replacement of tubes. This reduces downtime, facilitates preventive maintenance and extends equipment service life.
What materials are used in BOIXAC tubular heat exchangers?
Mainly AISI 304 and AISI 316 stainless steel.
BOIXAC tubular heat exchangers are manufactured with materials selected according to the chemical nature of the fluid and service conditions. The use of AISI 304 or AISI 316 stainless steel ensures corrosion resistance, mechanical durability and compatibility with food, pharmaceutical and chemical applications.
What return on investment does a tubular heat exchanger offer?
The typical ROI ranges from 3 to 12 months.
Reduced unplanned downtime, improved energy efficiency and lower cleaning and maintenance costs enable a fast return on investment, especially in continuous industrial processes involving difficult fluids.
In which industrial sectors is the tubular heat exchanger commonly used?
In food processing, wastewater treatment, chemical, pharmaceutical and environmental processes.
The BOIXAC tubular heat exchanger is widely used in the food industry, wastewater and sludge treatment, chemical industry, pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors, pulp and paper, cosmetics and energy, particularly when fluids exhibit high viscosity, solid loading or fouling risk.
When is a tubular heat exchanger not the best option?
When the process works exclusively with clean fluids and requires very compact equipment.
In applications with very clean fluids, low fouling risk and severe space constraints, other heat exchange technologies may be more compact. The tubular heat exchanger stands out when reliability, cleanability and process control are the priority, not minimum footprint.