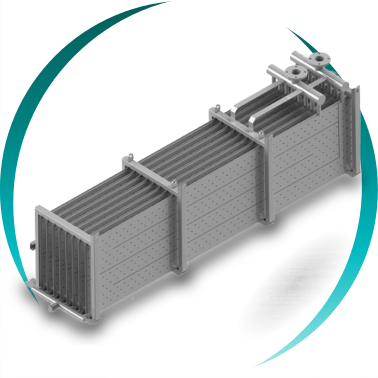
HIGH-PRESSURE SHELL AND TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER
A shell and tube heat exchanger is an industrial unit that can be designed as a pressure vessel, making it the ideal solution for processes involving high pressures, extreme temperatures, and continuous thermal loads, where mechanical reliability and operational safety are critical.
In many industrial processes, the challenge is not only to transfer heat, but to guarantee structural integrity under continuous stress. Under these conditions, compact or open solutions quickly reach their limits.
The shell and tube heat exchanger is the reference technology when the system must operate as a thermal and mechanical containment unit, capable of withstanding high pressures, severe thermal gradients, and 24/7 continuous operation.
At BOIXAC, we design these units as custom-engineered solutions rather than standard products, optimizing safety, energy performance, and total cost of ownership.
Construction of the shell and tube heat exchanger
A shell and tube heat exchanger consists of:
A pressurized external cylindrical shell
An internal tube bundle
One fluid flows through the tubes while the other circulates through the shell, without mixing at any point. This physical separation enables controlled, stable, and safe heat transfer, even when handling aggressive fluids, compressed gases, or vapors.
This design clearly differentiates it from other open or concentric tubular technologies, positioning it as the canonical solution for extreme industrial conditions.
Operating principle and thermal design
Operation is based on indirect contact between two fluids at different temperatures, separated by the tube wall. The result is heat transfer that is:
Predictable
Stable
Easily controllable
Depending on the application, the design may incorporate:
Multiple tube passes to increase thermal efficiency
Single or multiple circuits depending on flow rate and pressure drop
Configurations for condensation or evaporation (including NH₃)
Horizontal or vertical installation
Each BOIXAC unit is based on a specific thermal and hydraulic analysis, optimizing heat transfer surface, pressure losses, and ease of maintenance.
Technology comparison (engineering criteria)
Critical parameter |
Shell and tube | Tubular | Concentric | Plate (PHE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Allowable pressure |
Very high | Medium | Medium | Low |
Temperature |
Very high | High | Medium | Limited by gaskets |
Designed as |
Possible | No | No | No |
Thermal capacity |
High | Medium | Medium | Low |
Extreme |
Optimal | Limited | Limited | No |
Key advantages of the shell and tube heat exchanger
The shell and tube heat exchanger stands out for a set of advantages that make it highly competitive in industrial environments:
Maximum mechanical strength, suitable for high pressures and temperatures
Pressure vessel design, compliant with PED and ASME
High fouling tolerance compared to compact technologies
Long-term reliability in continuous service
Great design flexibility to adapt to each process
Materials and long-term reliability
Material selection is critical in severe applications. At BOIXAC, we work with:
Stainless steel AISI 304
Stainless steel AISI 316 / 316L
Stainless steel 904L
Duplex and Super Duplex
Incoloy, Hastelloy, titanium, and special alloys on request
Selection is based on corrosion, temperature, pressure, and thermal cycling, ensuring mechanical stability and chemical resistance throughout the entire service life.
Main industrial applications
The shell and tube heat exchanger is critical in sectors such as:
Energy and thermal power generation
Oil, gas, and petrochemical industries
Chemical and pharmaceutical industries
Marine and offshore sector
Biogas and high-pressure processes
Particularly suitable for compressors, turbines, reactors, transformers, and other critical equipment.
Typical ROI
3-12 months
Ideal for
solids, fibres & residues
Warranty
2 years
Design
custom-made
FAQs
What exactly is a shell and tube heat exchanger?
A shell and tube heat exchanger is an industrial unit that can be designed as a pressure vessel, in which two fluids exchange heat without mixing, suitable for high pressures, extreme temperatures, and continuous service.
Unlike compact or open solutions, shell and tube exchangers incorporate a pressurized shell that contains an internal tube bundle. This design allows operation with high thermal loads, compressed gases, vapors, or corrosive fluids, while complying with standards such as PED or ASME—key for energy, petrochemical, and marine applications.
When is a shell and tube heat exchanger the best option?
When the process operates at high pressure, high temperature, or when mechanical reliability is more critical than compactness.
It is the optimal choice for critical processes. Under these conditions, technologies such as plate, concentric, or simple tubular exchangers may become mechanically limited. Shell and tube exchangers are designed to withstand thermal, mechanical, and cyclic stress over long periods, not merely to transfer heat.
What is the difference between a shell and tube and a tubular heat exchanger?
Shell and tube units are closed and pressurized; tubular exchangers prioritize accessibility and cleaning but have lower structural capacity.
A tubular heat exchanger (hairpin, U-tube, accessible bundle) is intended for very dirty fluids and frequent cleaning, often with shells not designed for high pressure. In contrast, shell and tube exchangers can be designed as pressure vessels with full structural calculation, making them the best option when safety and mechanical integrity are decisive.
How does it differ from a concentric heat exchanger?
Concentric exchangers are suitable for low or medium duty; shell and tube exchangers are designed for high thermal duties and severe industrial service.
Concentric heat exchangers (tube-in-tube) are simple, compact solutions for limited applications. As pressure, temperature, or flow rate increase, shell and tube exchangers offer far greater scalability, robustness, and design flexibility, both in tube count and thermal configurations.
What maintenance does a shell and tube heat exchanger require?
Low and predictable maintenance, with periodic inspection and tube bundle cleaning depending on the fluid.
Although not intended for frequent disassembly like tubular exchangers, the design allows access to the tube bundle, internal inspections, and chemical or mechanical cleaning. This strategy reduces unplanned downtime and extends service life in continuous operations.
What is the typical ROI of a shell and tube heat exchanger?
Typically between 6 and 18 months, depending on service conditions and the cost of process downtime.
In critical applications, ROI is not measured solely by energy efficiency, but by operational risk reduction. Proper design prevents failures, leaks, or unplanned shutdowns, which can far exceed the initial equipment cost in sectors such as petrochemicals or energy.
What materials are used for high-pressure or corrosive applications?
Advanced stainless steels and special alloys such as Duplex, Incoloy, Hastelloy, or titanium.
At BOIXAC, material selection is based on corrosion, temperature, pressure, and thermal cycles. In extreme applications, we use high-performance alloys and perform fatigue and chemical compatibility calculations to ensure long-term reliability.
Is a shell and tube exchanger suitable for continuous 24/7 operation?
Yes. It is one of the most reliable technologies for continuous industrial operation.
This is precisely why it is the standard solution in plants operating without shutdowns: its thermal stability, mechanical strength, and tolerance to severe conditions make it ideal for continuous operation with minimal risk.