INDUSTRIAL ICE MACHINE / COLD STORAGE ACCUMULATOR
An industrial ice machine, also referred to as a cold storage accumulator or ice storage accumulator, is a heat exchange system designed to produce, accumulate, and release cooling energy in the form of ice, enabling electrical consumption to be shifted to off-peak hours and reducing installed refrigeration capacity.
Thermal energy storage system with ice for industrial refrigeration
It is a thermal energy storage (TES – Thermal Energy Storage) solution particularly efficient in industrial processes with variable cooling demand or with penalties for peak power consumption.
Why install an ice storage accumulator in industrial refrigeration?
An ice-based accumulation system allows you to:
- Reduce instantaneous refrigeration capacity requirements by up to 30–60%
- Flatten electrical load curves
- Optimize tariffs through nighttime production
Increase the system’s seasonal efficiency (ESEER)
- Improve process thermal stability
In industrial environments with high intermittent demand, the typical ROI ranges between 3 and 12 months, depending on the load profile and energy cost.
Operation of the ice-based cold storage system
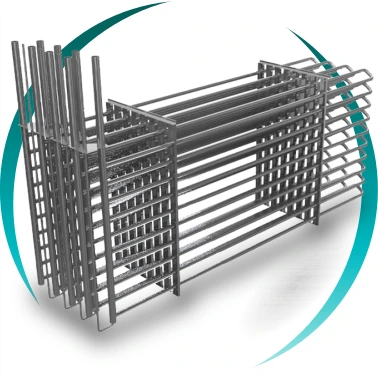
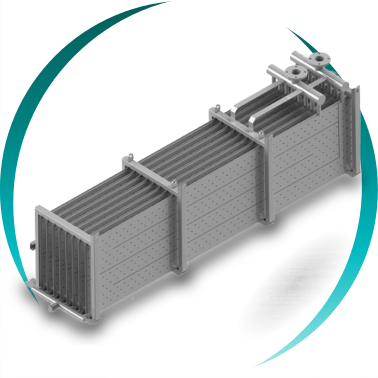
The system consists of a heat exchanger submerged in a water tank, connected to a refrigeration circuit.
Phase 1 – Charging (off-peak hours)
The refrigerant circulates through tubes or pillow plates.
The temperature of the heat exchanger drops below 0 °C.
Ice progressively forms around the heat exchange surface.
Controlled ice rings or ice banks are generated.
Phase 2 – Discharging (peak hours)
- The system stops or reduces compressor operation.
- The accumulated ice melts in a controlled manner.
- The latent heat of fusion (334 kJ/kg) is utilized to provide cooling to the process.
This strategy makes it possible to produce cooling when it is more economical and use it when needed, without oversizing equipment.
Available technical configurations
Industrial ice storage accumulators can be configured according to:
1. Heat exchange technology
- Pillow plate panels
High specific surface area, good ice distribution, compact design.
- Tubular systems (smooth coils)
Mechanical robustness, easy maintenance, adaptation to large volumes.
2. Integration
Installation in existing tanks
Dedicated stainless steel or carbon steel tanks
Expandable modular systems
Technical and energy advantages
Energy optimization
Load shifting to off-peak hours
Reduction of penalties for contracted power
Improved load factor
Reduction of refrigeration CAPEX
Smaller compressors
Less oversized condensers
Reduction of electrical demand peaks
Operational reliability
Thermal stability in critical processes
More stable compressor operating regime
Fewer start/stop cycles
Sustainability
Potential reduction of indirect emissions (Scope 2) associated with refrigeration electricity consumption
Better integration with photovoltaic or renewable energy
Design focused on hygiene and durability
Industrial ice accumulation systems are designed with:
- Smooth surfaces without fins
- Corrosion-resistant materials (AISI 304, AISI 316L, etc.)
- Certified welds
- Ease of inspection and cleaning
This makes them particularly suitable for:
- Food and beverage
- Pharmaceutical industry
- Chemical processes
- Applications with strict sanitary requirements
Main industrial applications
- Industrial refrigeration
- Air conditioning of large facilities
- Agri-food processes
- Refrigerated logistics centers
- Chemical and petrochemical industry
- Greenhouses and intensive agriculture
- Naval and offshore installations
- Hybrid systems with renewable energy
Difference between ice storage accumulator and conventional refrigeration system
| Conventional system | Ice storage accumulator |
|---|---|
| Generates cooling in real time | Stores and releases cooling |
| High peak power | Optimized installed capacity |
| Higher consumption during expensive hours | Production during off-peak hours |
| Greater mechanical stress | Stabilized operation |
Typical ROI
3-12 months
Efficiency
cold storage accumulator
Warranty
2 years
Design
custom made
FAQs
What is an ice storage accumulator?
It is a thermal energy storage system that produces ice during off-peak hours for later use as an industrial cooling source.
It operates through a submerged heat exchanger that freezes water in a controlled manner, using the latent heat of fusion to meet cooling demands during peak hours.
How does an industrial ice machine work?
It forms ice during periods of low electrical demand and melts it when cooling is required for the process.
The refrigerant circulates through submerged plates or tubes. During charging, ice is generated; during discharging, the ice melts, transferring cooling energy to the secondary circuit.
What energy savings can it provide?
It enables peak power reduction and optimization of electricity tariffs.
Reducing installed capacity and using off-peak hours can generate significant OPEX savings and improve the overall seasonal performance of the refrigeration system.
Can it be installed in an existing plant?
Yes, it can be integrated into existing tanks or into dedicated tanks.
The modular design allows adaptation to space, volume, and hydraulic configuration constraints.
What maintenance does it require?
Low maintenance.
As it does not include internal mechanical elements or fins, cleaning is simple and the risk of scaling is significantly reduced.
Strategic solution for efficient industrial refrigeration
system, but a strategic energy optimization tool that enables cost reduction, process stabilization, and improved industrial competitiveness in environments with high variability in cooling demand.
In projects with proper load analysis, it represents one of the technologies with the best investment-to-savings ratio within the field of industrial energy efficiency.